
Bakanae Disease of Rice: Symptoms, Disease Cycle, Management
Bakanae disease of Rice, also known as Fool’s rice, is a plant disease that affects rice crops. The term “Bakanae” comes from the Japanese phrase meaning “foolish seedling.” It causes the rice seedlings to appear weak, tall, and pale, often resulting in reduced yields. The Bakanae disease is caused by a fungus called Fusarium fujikuroi. In addition to rice, a similar disease called maize Fusarium kernel rot affects maize crops, causing rotting of kernels.
Table: Bakanae Disease of Rice Information
| Topic | Information |
|---|---|
| Disease Name | Bakanae disease (Fool’s rice) |
| Causal Organism | Fusarium fujikuroi (fungus) |
| Similar Disease in Maize | Maize Fusarium kernel rot |
| Symptoms | – Infected plants appear taller than normal plants – Thin plants with yellowish green leaves |
| – Drying symptoms in seedlings – Reduced tillering and drying of leaves during late infection | |
| – Partially filled, sterile, or empty grains on surviving infected plants | |
| – Lesions on roots of infected seedlings in the seedbed | |
| – Infected seedlings are elongated, slender, and slightly yellow compared to healthy seedlings | |
| – Infected plants grow up to three times taller than healthy plants | |
| – Early senescence and possible death before maturity | |
| – Empty panicles if infected plants survive to heading | |
| – Pink to white fungal growth at the base of infected plants | |
| Disease Cycle | – Pathogen: Gibberella fujikuroi |
| – Involves sexual and asexual reproduction | |
| – Sexual reproduction produces ascospores within asci | |
| – Asci are cylindrical structures containing 4 to 6 spores | |
| – Asexual reproduction produces hyphae, microconidia, macroconidia, and sclerotia | |
| – Sclerotia are dark blue, spherical structures | |
| – Stroma can vary in color from yellowish to brownish or violet | |
| Management Methods | – Izumonas: Fungicide for Rice Bakanae Disease with Pseudomonas Fluorescens |
| – Izumil: Fungicide for Rice Bakanae disease with extracts of Streptomyces griseus and Streptomyces violaceus | |
| Modes of Use | – Seed Treatment: Mix 5-10 ml of Izumonas and Izumil per kilogram of seeds |
| – Seedling Treatment: Dip roots in a solution of Izumonas and Izumil | |
| – Soil Application: Mix with farmyard manure or soil and apply before ploughing or irrigation | |
| – Foliar Application: Dilute and spray the foliage of the plants for complete coverage |
Bakanae Disease of Rice Symptoms:

- Infected plants appear several inches taller than normal plants in the seedbed and field.
- The infected plants are thin, with yellowish green leaves and pale green flag leaves.
- Seedlings show drying symptoms at early tillering stage.
- There is reduced tillering and drying of leaves during late infection.
- Surviving infected plants may have partially filled grains, sterile grains, or empty grains at maturity.
- In the seedbed, infected seedlings with lesions on roots may die before or after transplanting.
- Infected seedlings are elongated, slender, and slightly yellow compared to healthy seedlings.
- Infected plants grow up to three times taller than healthy plants, visibly arching above them.
- Infected plants senesce early and may die before reaching maturity.
- If infected plants survive to heading, they mostly produce empty panicles.
- The fungus infects the stems of the plants, and pink to white fungal growth appears at the base of infected plants.
- The cottony growth produces spores that contaminate healthy seeds during harvest.
Also Read: Rice Blast Disease: Symptoms, Signs, Disease Cycle and Management
Disease Cycle of Bakanae Disease of Rice:
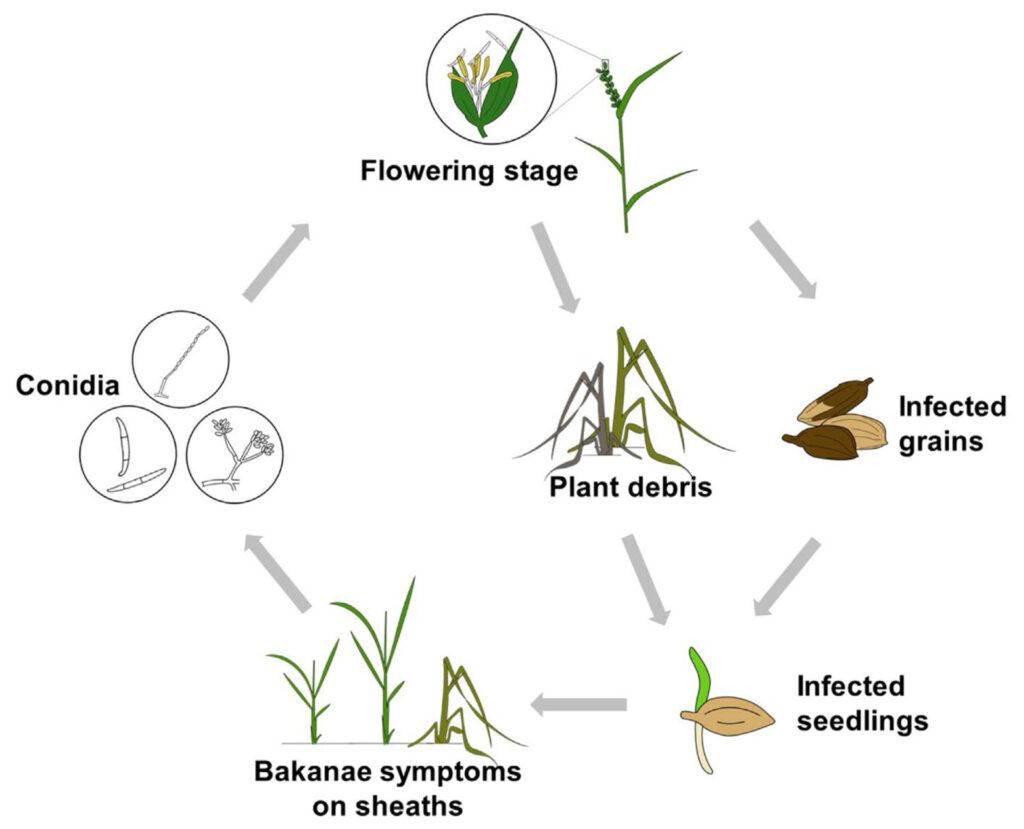
- The pathogen responsible for Bakanae disease of rice is Gibberella fujikuroi.
- The disease cycle of bakanae involves both sexual and asexual reproduction of the pathogen.
- The pathogen sexually produces ascospores, which are formed within a sac called an ascus.
- The asci are cylindrical, piston-shaped structures that are 90-102 x 7-9 µm in size.
- They typically contain 4 to 6 spores but rarely have 8 spores.
- The pathogen also produces hyphae, which are branched and septate.
- The fungus forms micro- and macro conidiophores that bear micro- and macroconidia, respectively.
- Sclerotia are another structure produced by the pathogen, measuring 80 x 100 µm.
- The sclerotia are dark blue, spherical structures.
- The stroma, which supports the reproductive structures, can vary in color, ranging from yellowish to brownish or violet.
Also Read: Sheath Rot Disease of Rice: Symptoms, Disease Cycle, Management
Bakanae Disease of Rice Management:
Preventing Method:
Izumonas-Best Fungicide

Izumonas (Bio Fungicides and Bactericides)
Contents: Pseudomonas Fluorescens
IZUMONAS is a biological product consisting of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR), which are naturally occurring bacteria found widely in nature. This unique product is designed to enhance plant defence mechanisms and promote healthy growth. IZUMONAS can be used on all types of crops without leaving any residue on the plants.
Izumil-Best Fungicide

Izumil (Bio Fungicides and Bactericides)
Contents:
- Extract of Streptomyces griseus: 30%
- Extract of Streptomyces violaceus: 40%
- Dissolving agents: 30%
IZUMIL is a remarkable biotech research product that has been developed to activate the natural defence mechanism of plants. By using IZUMIL, plants can better protect themselves against fungal pathogens, improve their physiological functions, and develop resistance against various harmful microorganisms. Similar to IZUMONAS, IZUMIL can be safely used on all crops without leaving any residue.
Modes of Use:
- Seed Treatment: Mix 5-10 ml of IZUMONAS and IZUMIL per kilogram of seeds in an adequate amount of water. Submerge the seeds in this solution and allow them to dry in a shaded area before sowing.
- Seedling Treatment: Combine 100 ml of IZUMONAS and IZUMIL per 20 litres of water. Dip the roots of the seedlings in this solution for approximately 30 minutes prior to transplanting.
- Soil Application: Mix 500 ml of IZUMONAS and IZUMIL with 30 kilograms of farmyard manure (FYM) or soil. Apply this mixture to one acre of land before ploughing or irrigation.
- Foliar Application: Dilute 2-3 ml of IZUMONAS and IZUMIL each in 1 litre of water. Use this solution to spray the entire foliage of the plants, ensuring complete coverage on both sides of the leaves. It is advisable to shake the bottle before use. For best results, spray early in the morning or evening. If a power sprayer is used, double the recommended dosage.
At the end, Bakanae disease is a significant crop disease caused by the fungus Fusarium fujikuroi. It leads to weak, tall, and pale rice seedlings, resulting in reduced yields. Effective management strategies, including the use of specialized fungicides like Izumonas and Izumil, can help mitigate the impact of this destructive disease. For further assistance or inquiries, please contact us directly.



